Impact of School Refusal: How It Affects Kids:
When a child constantly avoids going to school, it can have significant effects on different aspects of their life. Firstly, it can cause problems with their schoolwork, making it harder for them to do well academically. Additionally, avoiding school can lead to difficulties in forming and maintaining friendships, which are important for social development. Moreover, this pattern can create challenges within the family, including conflicts with parents and missed work days. Behind all of this, there are also emotional struggles like anxiety and sadness that contribute to school refusal.
Furthermore, the longer a child stays away from school, the more challenging it becomes to return. This means that the longer they avoid school, the harder it can be for them to catch up on missed learning and reintegrate into the school routine. It's essential to recognize that avoiding school doesn't just affect one area of a child's life; it has a ripple effect that touches their education, relationships, family dynamics, and emotional well-being.
Digging Deeper into School Refusal Causes
It's important to know that school refusal isn't just about a child skipping school for fun. Instead, it's a situation where a child strongly doesn't want to go to school at all.
Understanding School Refusal: Common Causes and Possible Reasons
Sometimes, there might be other reasons why a child doesn't want to go to school. These could include:
- Bullying: If a child is being treated badly by others, they might not want to go to school.
- School Challenges: If they're finding schoolwork tough, it could make them want to avoid going.
- Feeling Nervous: They might be worried about a test, a speech, or something else happening at school.
- Life Changes: Big events like moving, having a new sibling, or family changes can make school hard to handle.
- Emotional Struggles: Feelings like being too worried, sad, or not being able to handle social situations can lead to avoiding school.
- Physical Complaints: If they often say they're sick, like having headaches or stomach aches, it might be a way to not go to school.
Remember, there could be more to the story when a child doesn't want to go to school.
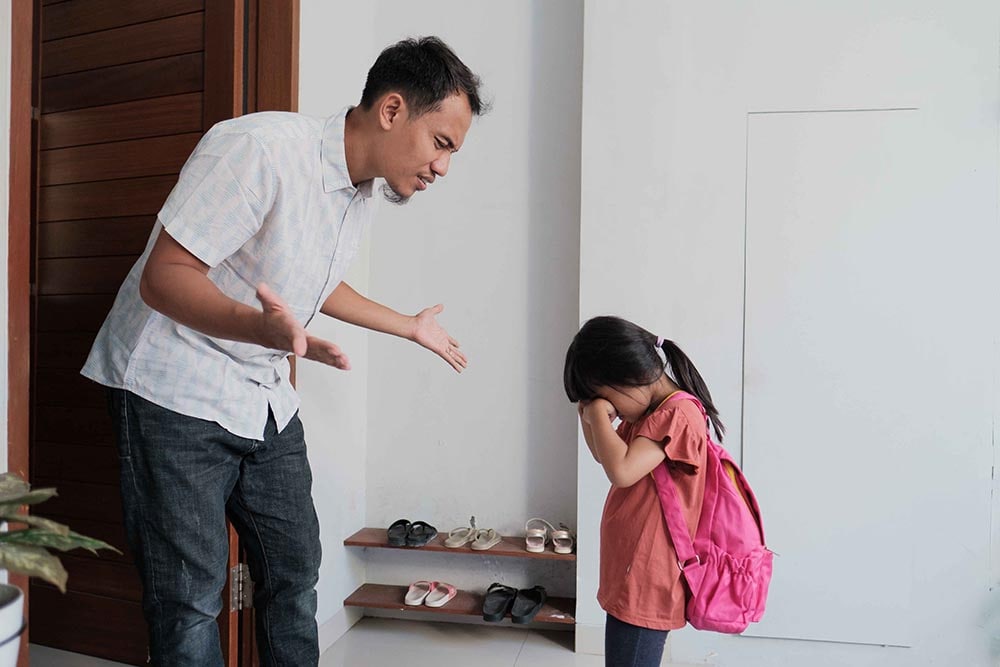

How can we help with school refusal?
When a child keeps avoiding school for a while, like days, weeks, or even months, there are ways to help them. This can include getting them back to school and helping with things like anxiety or similar.
We have plans to help with school refusal. The plans are different depending on how serious it is: mild, moderate, or serious. The cost and how long it takes are different for each person, but usually, the treatment goes on for about six weeks.
Step 1: Understanding Why a Child Doesn't Want to Go to School
In this first step, we carefully examine why a child is avoiding school. A specialized therapist will be involved in this process.
- Thorough Discussion: The therapist will have a detailed conversation with the child and their parents. They might also talk to teachers, caregivers, and school staff.
- Gathering Information: We'll collect important information. We'll talk to the student and their parents, and possibly teachers or others involved. We'll use tools like ratings and scales to help. We might also observe the child at school or home, either in person or through remote methods.
- Checking Health: Sometimes, we might need to get a doctor's opinion to understand better.
This step is crucial to know what's causing the child's hesitation about going to school.
Step 2: Customized Advice and a Well-Planned Treatment
Treatment plans require consistent, dedicated planning and implementation to ensure the behavior is discontinued.
Treatment plans for students may include:
- Taking Small Steps: Students can get used to school by spending a bit of time there every day and gradually getting used to it.
- Learning to Relax: If a student feels nervous about school or talking to friends, they can learn ways to stay calm.
- Making Friends: Students can also learn how to be better at making friends and getting along with others.
- Earning Rewards: Going to school regularly can earn students cool rewards, which makes it more fun.
- Setting Goals: Students can decide on things they want to achieve at school and work towards them.
- Positive Thinking: When students worry, they can learn how to think in helpful and positive ways.
Parent/School training may include:
- Smoother Days: Making mornings and evenings easier by having a routine.
- Catching the Good: Giving attention when students do well and come to school. Making it not fun if they don't come. Not paying attention to bad behavior.
- Time for School: Not letting the child do fun things like watch TV or play games when it's time for school.
- Communication skills training: Learning how to talk so there's less fighting at home.
Please contact us for more information or to schedule a consultation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the effects of school refusal on a child's life?
School refusal can have significant impacts on various aspects of a child's life. It can lead to academic difficulties, challenges in forming and maintaining friendships, conflicts within the family, and emotional struggles like anxiety and sadness. The longer a child avoids school, the harder it becomes for them to catch up on missed learning and reintegrate into the school routine. Avoiding school has a ripple effect that affects education, relationships, family dynamics, and emotional well-being.
What are the common causes of school refusal?
School refusal is often not just about a child skipping school for fun. Common causes and possible reasons include:
- Bullying
- School Challenges
- Feeling Nervous:
- Life Changes
- Emotional Struggles
- Physical Complaints
Can school refusal be prevented?
While it may not always be preventable, early intervention is crucial. We try to help parents create a supportive environment, address academic or social difficulties promptly, and provide emotional support to help reduce the risk of school refusal.
How can we help a child with school refusal?
When a child constantly avoids school for an extended period, there are ways to help them. The process may include getting them back to school and addressing issues like anxiety. The treatment plans vary based on the severity of the situation (mild, moderate, or severe) and typically last for about six weeks.