Behavior Therapy for ADHD: A Guide to Effective Strategies for Children
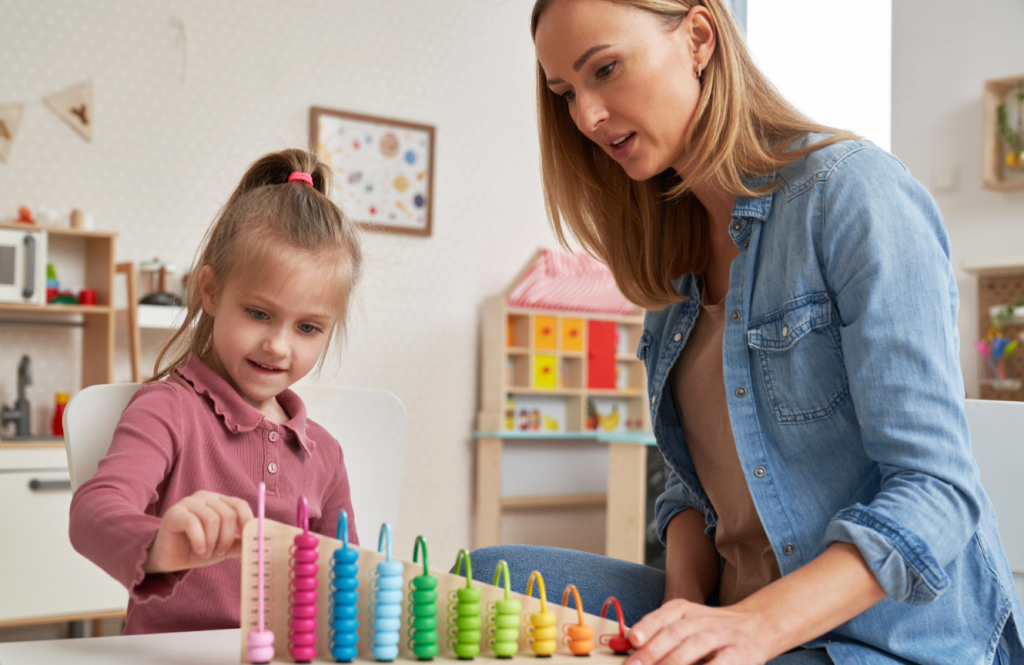

Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects millions of children, making it difficult for them to regulate emotions, follow instructions, and manage daily routines. While ADHD medication can be an important part of treatment, research shows that behavior therapy works effectively in helping children develop skills for long-term success. Behavior management strategies, particularly behavioral parent training, empower families with the tools to reinforce positive behavior and reduce problem behaviors at home, in school, and in social settings.
What is Behavior Therapy for ADHD?
Behavior therapy is an evidence-based approach designed to help children with ADHD learn self-control, improve their social interactions, and succeed in structured environments. This form of therapy focuses on teaching children and their caregivers how to manage behavior effectively, using techniques such as positive reinforcement, structured routines, and stress management strategies.
For school-aged children, behavior therapy is often recommended as a first-line treatment alongside or before considering ADHD medication. Studies have shown that when combined with training parents and educators, behavior therapy significantly improves daily functioning and overall quality of life for children with ADHD.
How Behavior Therapy Works
Behavior therapy is most effective when parents, teachers, and caregivers work together to create consistent, structured environments that support a child’s ability to succeed. Here are some key elements of how it works:
1. Training Parents to Reinforce Positive Behavior
One of the most impactful parts of behavior therapy is training parents to implement strategies that encourage desired behavior and reduce impulsivity. Parenting programs, such as the Positive Parenting Program (Triple P) and Behavioral Parent Training (BPT), focus on teaching parents how to:
- Use positive reinforcement (praising good behavior instead of punishing negative behavior).
- Set clear expectations and follow through with consistent consequences.
- Establish effective discipline strategies that are proactive rather than reactive.
- Create a structured environment with predictable routines.
By reinforcing positive behavior, parents can help their child build self-confidence and improve their ability to regulate emotions and actions.
2. Teaching Children Self-Regulation Strategies

For a young child with ADHD, learning how to control impulses and emotions can be challenging. Behavior therapy teaches children how to:
- Recognize and manage big emotions such as frustration or anxiety.
- Use deep breathing and relaxation techniques to calm themselves in stressful situations.
- Practice problem-solving skills when facing challenges in school or at home.
- Improve motor skills and coordination through structured activities that enhance focus and self-control.
These strategies not only help children in the moment but also contribute to long-term emotional and social development.
3. Building Effective Routines for School-Age Children
Children with ADHD thrive in environments with clear expectations and predictable routines. Therapists work with families to create daily schedules that:
- Minimize distractions during homework and study time.
- Include physical activity to help regulate energy levels and release endorphins.
- Implement stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and scheduled breaks.
- Encourage school-aged children to take responsibility for small tasks, such as packing their school bag the night before.
By providing structure, children feel more secure, reducing frustration and improving overall behavior.
The Role of Schools and Educators in Behavior Therapy
Because children spend a significant portion of their day in school, educators play a key role in implementing behavior management strategies. School-based interventions for ADHD include:
- Developing Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) or 504 Plans to provide academic accommodations.
- Using visual schedules, timers, and task lists to improve focus and task completion.
- Encouraging movement breaks to reduce restlessness and improve concentration.
- Collaborating with parents and therapists to ensure consistency between home and school environments.

Long-Term Benefits of Behavior Therapy
Unlike medication, which primarily manages symptoms in the short term, behavior therapy provides children with skills that last a lifetime. Some of the long-term benefits include:
- Improved social interactions and friendships.
- Increased academic success and better classroom behavior.
- Greater self-control and emotional regulation.
- Reduced family stress and improved parent-child relationships.
- Lower risk of developing anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem due to ongoing behavioral challenges.
When to Seek Professional Support
If your child’s ADHD symptoms are interfering with daily life at home or school, seeking professional support can help. A structured behavior therapy program, combined with training parents and school-based interventions, can set children up for success.
At Manhattan Psychology Group, we specialize in behavior therapy for ADHD, offering tailored support for young children with ADHD and school-age children. Our team provides evidence-based interventions that teach families how to create structured, supportive environments that promote growth and success.
We proudly serve families in New York City, including Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, and surrounding areas. Contact us today to learn more about our ADHD treatment programs and how we can help your child thrive.