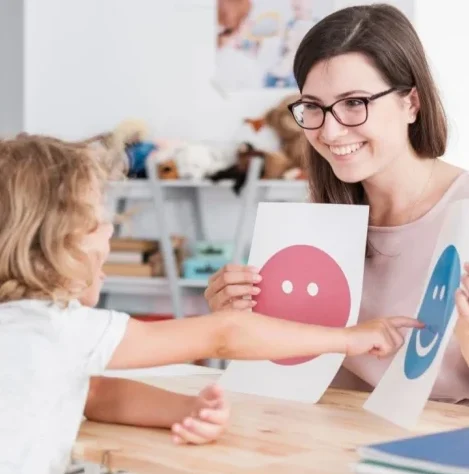
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that presents a unique set of challenges for individuals, impacting their ability to focus, regulate behavior, and navigate social interactions.
While medication is a common treatment approach, behavior therapy has emerged as a powerful complementary intervention, offering a comprehensive and personalized approach to addressing the multifaceted aspects of ADHD.
ADHD: The Core Challenges
ADHD is characterized by a constellation of symptoms that can manifest in varying degrees of severity. At its core, individuals with ADHD often grapple with inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, which can significantly impact their daily functioning and development.
- Inattention: The individual may find it challenging to sustain focus on tasks, easily becoming distracted and struggling to pay attention to matters that require prolonged concentration.
- Hyperactivity: Characterized by excessive physical movement, fidgeting, and an inability to remain still, hyperactivity can disrupt learning and social environments. Impulsivity: Individuals with ADHD may exhibit impulsive behaviors, such as interrupting others, acting without considering consequences, and having difficulty waiting their turn.
While these core symptoms are the hallmarks of ADHD, the condition can also manifest in other ways, such as difficulty completing daily tasks, appearing inattentive when spoken to, struggling with organization, and losing essential materials. It is crucial to recognize that the severity of ADHD can range from mild to severe, and a comprehensive assessment is necessary to determine the most appropriate course of treatment.
The Ripple Effect: Associated Behavioral Challenges
Untreated ADHD can have far-reaching consequences, extending beyond the core symptoms and potentially leading to the development of associated behavioral disorders. Children with ADHD are more susceptible to conditions like Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) and Conduct Disorder (CD), which can further exacerbate the challenges they face.
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD): Children with ODD may exhibit defiant behaviors, such as arguing with adults, losing their temper, and deliberately antagonizing others.
- Conduct Disorder (CD): Characterized by more severe behavioral issues and aggression, CD can manifest in behaviors like lying, stealing, breaking rules, and causing harm to others or animals.
These associated disorders can significantly impact the individual's ability to form and maintain healthy relationships, as well as their overall well-being and quality of life.
Introducing Behavior Therapy: A Comprehensive Approach
Behavior therapy is a widely recognized and evidence-based intervention that has proven effective in managing a range of behavioral and developmental challenges, including ADHD. At its core, behavior therapy focuses on modifying behaviors through a systematic approach that involves observation, assessment, and the implementation of targeted interventions.
The Power of Positive Reinforcement
One of the key principles of behavior therapy is the use of positive reinforcement, which involves rewarding desired behaviors to increase their likelihood of occurring in the future. This approach can be particularly effective in addressing the core symptoms of ADHD, such as inattention and impulsivity.
By providing positive reinforcement when an individual with ADHD demonstrates focus, completes tasks, or exhibits appropriate social behaviors, the therapy reinforces these positive patterns and encourages their repetition. This positive reinforcement can take various forms, such as verbal praise, tangible rewards, or access to preferred activities.
Breaking Down Complex Behaviors
Another strength of behavior therapy lies in its ability to break down complex behaviors into manageable steps, a process known as task analysis. This approach can be particularly beneficial for individuals with ADHD who may struggle with completing multi-step tasks or following instructions.
By breaking down a task into smaller, more manageable components, behavior therapists can guide the individual through each step, providing prompts, reinforcement, and support as needed. This gradual approach not only increases the likelihood of task completion but also fosters a sense of accomplishment and builds confidence.
Fostering Social Skills and Self-Management
Individuals with ADHD often face challenges in social situations, as they may struggle with interpreting social cues, regulating their behavior, and engaging in appropriate interactions. Behavior therapy addresses these challenges through social skills training and self-management techniques.
- Social Skills Training: Through role-playing, modeling, and the use of social stories, behavior therapists can teach individuals with ADHD how to interpret social cues, understand perspectives, and develop appropriate communication and interaction strategies.
- Self-Management Training: Behavior therapy equips individuals with ADHD with self-awareness and self-monitoring skills, empowering them to recognize and manage their own behaviors more effectively.
By developing these essential social and self-management skills, individuals with ADHD can improve their ability to navigate social situations, build and maintain healthy relationships, and ultimately enhance their overall quality of life.

Tailoring Interventions: A Personalized Approach
One of the strengths of behavior therapy lies in its ability to tailor interventions to the unique needs and challenges of each individual. Through comprehensive assessments and ongoing observation, behavior therapists can identify specific areas of concern and develop personalized treatment plans that target those areas.
For example, if an individual with ADHD struggles with completing homework assignments, the behavior therapist may implement organizational skills training and develop strategies for breaking down assignments into manageable steps. Alternatively, if the primary challenge is impulsivity, the therapist may focus on teaching coping strategies and techniques for self-regulation.
Collaboration and Consistency: Keys to Success
Effective behavior therapy for ADHD relies on a collaborative approach that involves not only the therapist but also caregivers, educators, and the individual themselves. By working together as a team, everyone involved can ensure that the strategies and techniques learned during therapy sessions are consistently applied across different environments, such as home and school.
Regular communication and coordination among all parties involved are essential for tracking progress, identifying areas for improvement, and making data-driven adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. This collaborative approach not only maximizes the effectiveness of the therapy but also fosters a supportive and consistent environment for the individual with ADHD.
Measuring Progress and Celebrating Achievements

Evaluating the effectiveness of behavior therapy for ADHD involves a comprehensive approach that combines quantitative and qualitative measures. Standardized behavior rating scales, direct observation, and self-reporting can provide valuable insights into the individual's progress, allowing therapists and caregivers to track changes in core ADHD symptoms, such as impulsivity, attention span, and task completion.
It is important to recognize that progress may not always be linear or immediate, as behavior change is a gradual process that requires consistent effort and reinforcement. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary to ensure that the therapy remains effective and aligned with the individual's evolving needs.
Celebrating achievements, no matter how small, is crucial in maintaining motivation and fostering a positive mindset. By acknowledging and reinforcing positive changes in behavior, Behavior therapy can help individuals with ADHD develop a sense of accomplishment and build confidence in their ability to manage their symptoms and thrive.
Long-Term Benefits: Paving the Way for Success
The benefits of behavior therapy for ADHD extend far beyond the immediate management of symptoms. By equipping individuals with essential life skills, such as organization, time management, and effective communication, behavior therapy can pave the way for long-term success in various aspects of life.
- Academic Achievement: Improved focus, organization, and task completion skills can significantly enhance academic performance, leading to better grades and increased confidence in educational settings.
- Social Relationships: Developed social skills and emotional regulation strategies can foster healthier and more fulfilling relationships with peers, family members, and others.
- Independence and Self-Advocacy: Self-management and self-awareness skills empower individuals with ADHD to take an active role in their own well-being and advocate for their needs effectively.
By addressing the core challenges of ADHD and providing individuals with the tools and strategies necessary to navigate daily life, behavior therapy can unlock their full potential and set them on a path towards thriving and reaching their goals.
Embracing a Holistic Approach: Combining behavior therapy with other interventions
While behavior therapy is a powerful intervention for ADHD, it is often most effective when combined with other evidence-based approaches, such as medication management, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and family therapy. This holistic approach recognizes the multifaceted nature of ADHD and addresses the various aspects of the condition, ensuring a comprehensive and well-rounded treatment plan.
By working closely with healthcare professionals, therapists, and caregivers, individuals with ADHD can benefit from a tailored and integrated approach that addresses their unique needs and circumstances. This collaborative effort not only maximizes the effectiveness of the interventions but also fosters a supportive and nurturing environment that promotes long-term success and well-being.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals with ADHD to Thrive
ADHD presents a unique set of challenges, but with the right interventions and support, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and unlock their full potential. Behavior therapy, with its focus on behavior modification, positive reinforcement, and personalized strategies, has proven to be an effective approach in addressing the core symptoms of ADHD and associated behavioral challenges.
By fostering essential life skills, improving focus and concentration, and promoting positive habits, behavior therapy empowers individuals with ADHD to navigate daily life with greater ease and confidence. Whether it's enhancing academic performance, building healthier social relationships, or developing self-advocacy skills, behavior therapy provides a comprehensive framework for personal growth and success.
As we continue to deepen our understanding of ADHD and refine our interventions, it is crucial to embrace a holistic and individualized approach that recognizes the unique strengths and challenges of each person. By combining behavior therapy with other evidence-based interventions and fostering a collaborative and supportive environment, we can empower individuals with ADHD to thrive, reach their full potential, and live fulfilling lives.